Understanding Vision Testing: Importance and Procedures
Vision testing is a crucial component of maintaining eye health and ensuring clear vision. Regular vision tests can help detect potential problems early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. This article will explore the importance of vision testing, the different types of tests available, and how they contribute to overall eye health.
The Importance of Vision Testing
Vision is one of the most critical senses, and maintaining good eye health is essential for overall well-being. Regular vision testing plays a vital role in:
- Early Eye Condition Detection: In their early stages, many eye problems, including glaucoma, cataracts, and macular degeneration, can develop without any obvious symptoms. Regular vision tests can detect these conditions early, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further damage.
- Correcting Vision Problems: Vision testing can identify refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), astigmatism, and presbyopia. These issues can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or surgery, improving the quality of life.
- Preventing Eye Strain: With the increased use of digital devices, eye strain has become a common problem. Regular vision testing can help identify the need for corrective lenses or changes in screen habits to reduce eye strain.
- Monitoring Eye Health: Vision tests provide valuable information about the overall health of the eyes. Regular check-ups can help monitor changes in vision and detect any signs of disease or deterioration.
Types of Vision Tests
Vision testing encompasses a variety of tests designed to assess different aspects of eye health and visual acuity. Here are some of the most common types of vision tests:
- Visual Acuity Test: This is one of the most basic and common vision tests, used to measure how clearly you can see. During this test, you’ll be asked to read letters from a chart (Snellen chart) placed at a certain distance. The results will determine your visual acuity, usually expressed as a fraction (e.g., 20/20 vision).
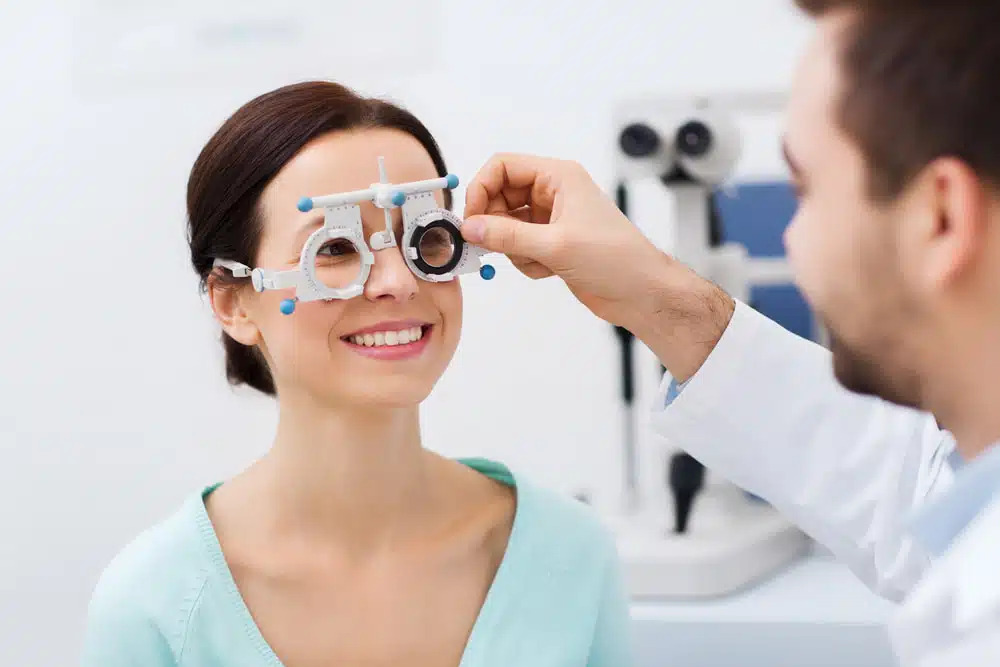
- Refraction Test: This test is used to determine the correct prescription for glasses or contact lenses. The eye doctor will use a device called a phoropter to place a series of lenses in front of your eyes and ask you to identify which lens gives you the clearest vision.
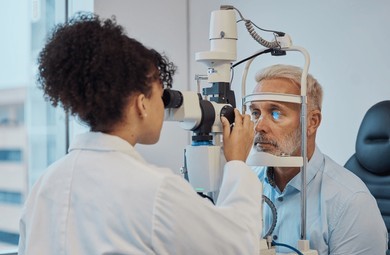
- Slit-Lamp Examination: A slit-lamp is a microscope with a bright light used to examine the structures of the eye, including the cornea, iris, lens, and retina. This test helps detect eye conditions such as cataracts, macular degeneration, and corneal injuries.
- Pupil Dilation: During this test, eye drops are used to dilate the pupils, allowing the doctor to examine the retina and optic nerve more thoroughly. This is particularly useful for detecting conditions like diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and glaucoma.
- Tonometry: Tonometry measures the pressure inside the eye, which is an important factor in detecting glaucoma. The most common method involves a puff of air being directed at the eye, which measures the eye’s resistance to the air pressure.
- Visual Field Test: This test assesses your peripheral (side) vision and can detect blind spots that may indicate eye conditions like glaucoma, retinal diseases, or optic nerve damage.
- Color Vision Test: This test checks for color blindness, which is the inability to perceive certain colors correctly. You’ll be shown a series of colored patterns and asked to identify numbers or shapes within them.
- Ocular Motility Test: This test evaluates the movement of your eyes and how well they work together. It helps in diagnosing issues like strabismus (crossed eyes) or amblyopia (lazy eye).
- Retinal Imaging: This involves taking digital images of the retina, which can help in diagnosing and monitoring conditions like diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, and retinal detachment.
- Keratometry: This test measures the curvature of the cornea and is particularly important for fitting contact lenses and diagnosing astigmatism.
How Vision Testing Contributes to Overall Health
Regular vision testing is not just about maintaining good eyesight; it also plays a significant role in overall health. Here’s how:
- Detection of Systemic Diseases: The eyes are often referred to as the “windows to the soul,” but they can also be windows to your overall health. Eye exams can detect signs of systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol. For example, diabetic retinopathy is a complication of diabetes that can be detected through an eye exam.
- Preventing Vision Loss: Many eye conditions, if left untreated, can lead to permanent vision loss. Regular vision testing allows for early detection and treatment, reducing the risk of vision loss.
- Enhancing Quality of Life: For daily tasks including reading, driving, working, and engaging in hobbies, clear vision is necessary. Vision testing ensures that any refractive errors are corrected, enhancing the overall quality of life.
- Supporting Mental Health: Poor vision can lead to difficulties in performing daily tasks, which can, in turn, lead to frustration, anxiety, and depression. By maintaining good eye health, individuals can support their mental well-being.
Who Should Get Vision Testing?
Vision testing is essential for people of all ages. Here’s a breakdown of when and why different age groups should have their vision tested:
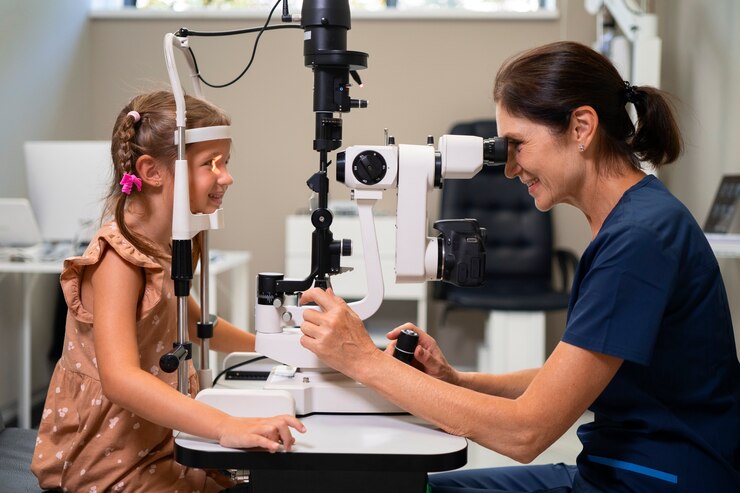
- Children: Early detection of vision problems in children is crucial for their development. Children should have their first comprehensive eye exam at around six months of age, another at three years, and then before starting school. Regular check-ups are important, especially if the child shows signs of vision problems, such as squinting or sitting too close to the television.
- Adults (18-60 years): Adults should have a comprehensive eye exam every two years, or more frequently if they have vision problems or wear glasses or contact lenses. Regular testing is important to monitor changes in vision and detect eye conditions that may develop with age.
- Seniors (60+ years): As people age, the risk of eye conditions such as cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration increases. Seniors should have an eye exam annually to monitor for these conditions and maintain good vision health.
- People with Diabetes or Hypertension: Individuals with diabetes or hypertension should have regular vision tests, as these conditions increase the risk of developing eye diseases like diabetic retinopathy and hypertensive retinopathy.
- Individuals with a Family History of Eye Disease: If you have a family history of eye conditions like glaucoma, macular degeneration, or retinal detachment, regular vision testing is essential for early detection and prevention.
Conclusion
Vision testing is a critical aspect of maintaining eye health and overall well-being. Regular eye exams can detect vision problems early, prevent vision loss, and even uncover signs of systemic diseases. Regardless of age or current eye health, everyone should prioritize regular vision testing as part of their healthcare routine. By doing so, you can ensure that your eyes remain healthy and that you continue to enjoy clear, sharp vision for years to come.
For any further queries, Plz visit drvivekgarg. in