Global Trends In Cataract Surgery: Addressing Access And Quality Of Care
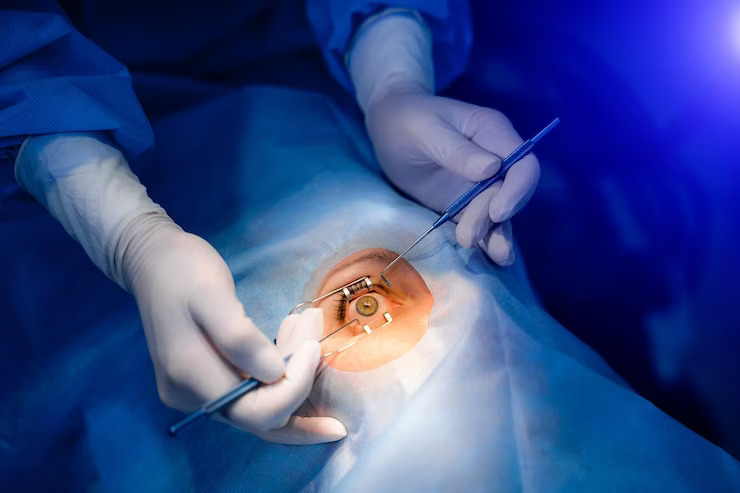
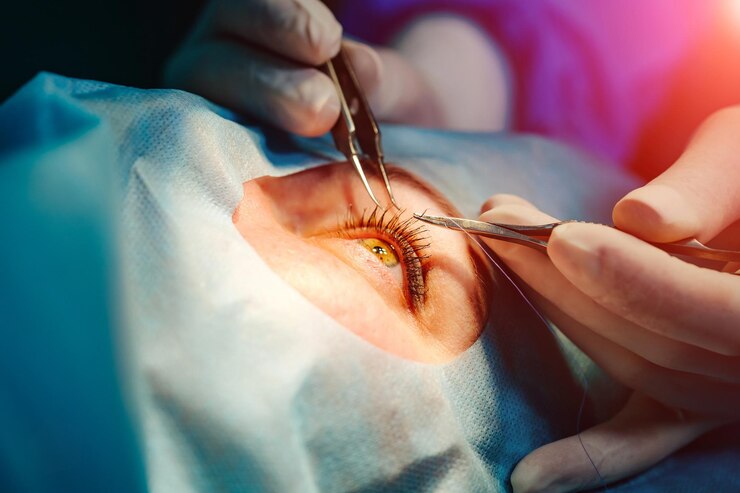
Cataract surgery stands as one of the most common and successful medical procedures, offering the restoration of vision for millions worldwide. However, despite its efficacy, access to quality cataract surgery remains unequal across different regions, posing significant challenges to global eye health. In this article, we explore the current global trends in cataract surgery, examining efforts to enhance accessibility, improve quality of care, and address disparities in eye health outcomes.
The Burden of Cataract Blindness
Cataracts, characterized by the clouding of the eye’s lens, are a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cataracts are responsible for approximately 51% of world blindness, affecting an estimated 65 million people worldwide. The burden of cataract blindness disproportionately affects low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), where access to eye care services and surgical interventions may be limited.
Global Initiatives for Cataract Elimination
In recent years, there has been a concerted effort by international organizations, governments, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) to eliminate avoidable blindness due to cataracts. The WHO’s Vision 2020 initiative, launched in collaboration with the International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness (IAPB) and other partners, aims to eliminate avoidable blindness by the year 2020, with a particular focus on cataract surgical services.
Through Vision 2020 and subsequent initiatives, significant progress has been made in expanding access to cataract surgery in underserved regions. Outreach programs, community-based screening campaigns, and surgical camps have helped identify individuals with cataracts and provide them with timely access to sight-restoring interventions.
Technological Innovations and Surgical Advances
Advancements in cataract surgery techniques and technologies have played a pivotal role in improving surgical outcomes and expanding access to care. Phacoemulsification, the most commonly performed cataract surgery technique, offers smaller incisions, faster recovery times, and reduced risk of complications compared to traditional extracapsular cataract extraction.
Furthermore, the development of affordable and portable phacoemulsification machines has facilitated the establishment of cataract surgical centers in resource-limited settings. These technological innovations have enabled surgeons to perform high-quality cataract surgery with minimal infrastructure requirements, thus increasing accessibility for underserved populations.
Addressing Disparities in Access
Despite these advancements, disparities in access to cataract surgery persist, particularly in rural and remote areas of LMICs. Barriers to access include geographical isolation, lack of transportation, financial constraints, and cultural beliefs surrounding eye health and surgical interventions.
To address these disparities, innovative approaches such as teleophthalmology, mobile eye care units, and task-shifting strategies have been employed to extend eye care services to underserved populations. Teleophthalmology allows for remote diagnosis and consultation, enabling primary care providers to identify and refer individuals in need of cataract surgery to specialized facilities.
Quality Assurance and Capacity Building
Ensuring the quality of cataract surgical services is essential for achieving successful outcomes and minimizing the risk of complications. Quality assurance measures, including surgeon training and accreditation programs, adherence to surgical protocols, and monitoring of surgical outcomes, are critical for maintaining high standards of care.
Capacity-building initiatives that focus on training local healthcare providers in cataract surgery techniques and postoperative care play a vital role in strengthening health systems and reducing reliance on external assistance. By empowering local surgeons and healthcare professionals, sustainable eye care services can be established, leading to improved access and quality of cataract surgery in underserved regions.
Conclusion
Cataract surgery remains a cornerstone of global eye health efforts, offering a cost-effective and transformative intervention for individuals affected by vision impairment and blindness. While significant progress has been made in expanding access to cataract surgical services, challenges persist in ensuring equitable access and quality of care, particularly in low-resource settings.
Addressing disparities in access to cataract surgery requires a multi-faceted approach that combines technological innovation, community engagement, capacity building, and policy support. By working collaboratively across sectors and leveraging resources effectively, we can strive towards the goal of eliminating avoidable blindness due to cataracts and ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their geographic location or socioeconomic status, have access to sight-restoring interventions. Global trends in cataract surgery underscore the importance of collective action and sustained commitment to achieving universal eye health coverage for all.