Digital Eye Strain Assessment: Addressing The Impact Of Screen Time
In today’s digital age, the prevalence of screen-based devices such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and televisions has become ubiquitous. While these devices offer convenience, connectivity, and productivity, prolonged use can lead to a range of visual discomfort and symptoms collectively known as digital eye strain. This article aims to explore the causes, symptoms, assessment methods, and strategies for addressing digital eye strain in the modern era.
Understanding Digital Eye Strain
Digital eye strain, also referred to as computer vision syndrome or digital fatigue, is a condition characterized by a cluster of symptoms that occur after prolonged use of digital devices. These symptoms may include:
- Eye fatigue or tiredness
- Dry or irritated eyes
- Blurred or double vision
- Headaches
- Neck and shoulder pain
- Difficulty focusing
- Sensitivity to light
The prevalence of digital eye strain has surged in recent years, affecting individuals of all ages who spend extended periods in front of screens for work, education, entertainment, and communication. Factors contributing to digital eye strain include prolonged screen exposure, poor lighting conditions, improper viewing distances, and poor posture.
Assessment Methods for Digital Eye Strain
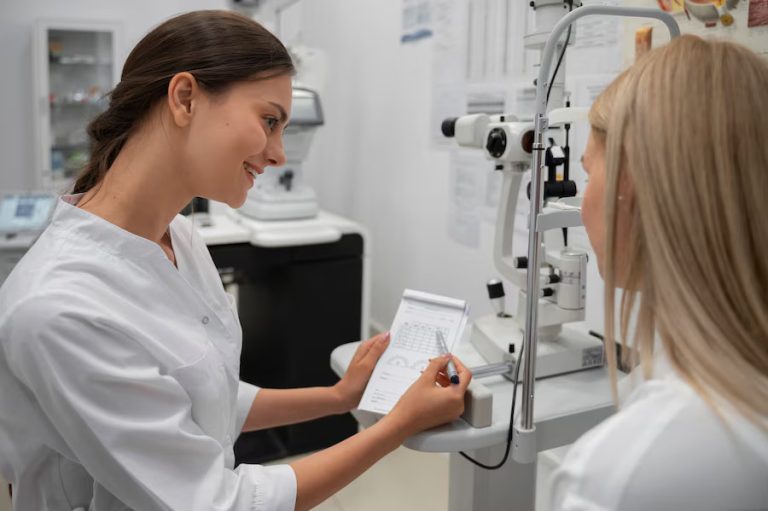
Assessing digital eye strain involves a comprehensive evaluation of visual symptoms, ergonomic factors, and digital device usage habits. Healthcare providers, including optometrists and ophthalmologists, employ various assessment methods to diagnose and manage digital eye strain effectively.
Symptom Questionnaires: Healthcare providers may use standardized questionnaires to assess the severity and frequency of digital eye strain symptoms reported by patients. These questionnaires help identify specific visual discomforts and guide treatment recommendations.
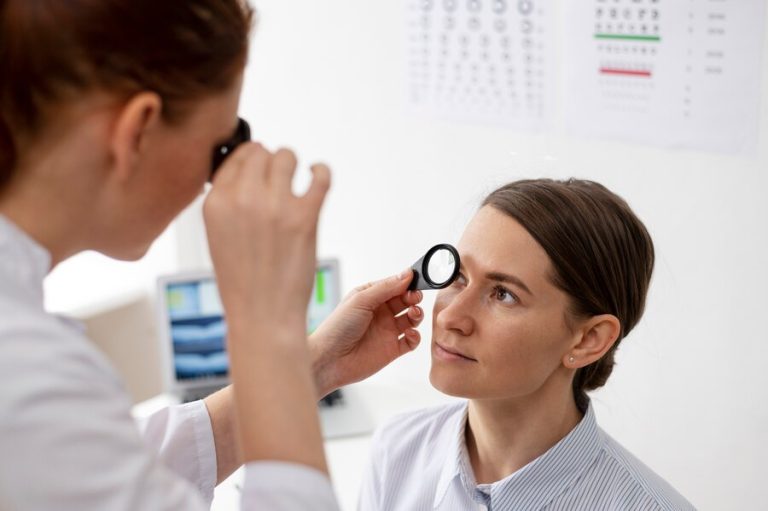
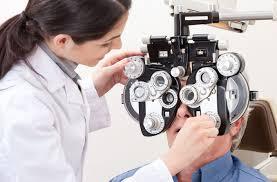
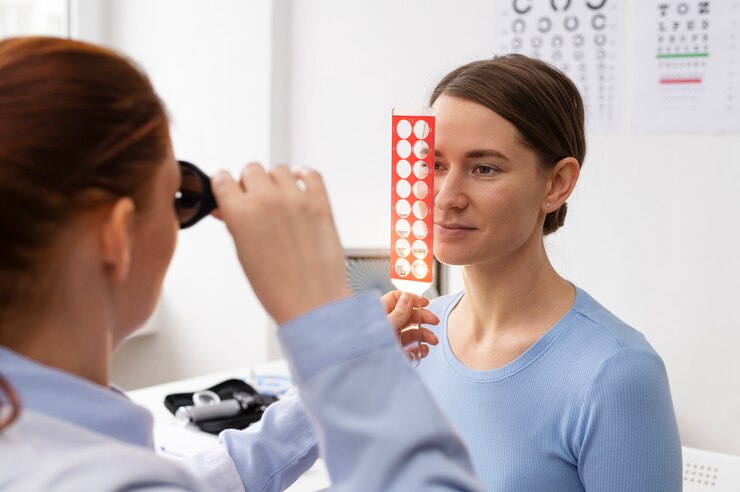
Visual Acuity Testing: Visual acuity testing measures the clarity and sharpness of vision at various distances. Individuals experiencing digital eye strain may exhibit changes in visual acuity, such as blurred vision or difficulty focusing, which can be detected through comprehensive eye examinations.
Refraction Assessment: Refraction assessment determines the need for corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, to optimize visual acuity and reduce digital eye strain symptoms. Refractive errors, such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism, can exacerbate visual discomfort when viewing digital screens.
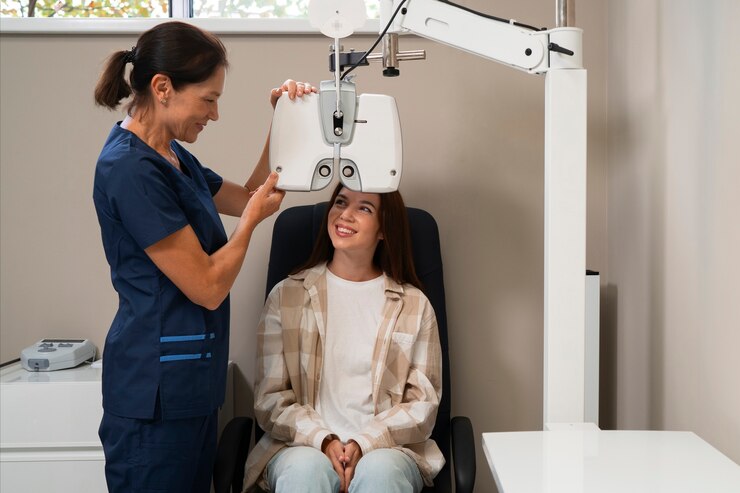
Ergonomic Evaluation: Ergonomic evaluation assesses the workplace or home environment to identify factors contributing to digital eye strain, including screen placement, lighting conditions, seating posture, and viewing distances. Making ergonomic adjustments can alleviate visual discomfort and promote comfortable screen use.
Blue Light Exposure Measurement: Blue light emitted by digital screens has been implicated in digital eye strain and may disrupt sleep-wake cycles and circadian rhythms. Specialized instruments can measure blue light exposure and recommend protective measures, such as blue light-filtering glasses or screen filters, to reduce eye strain.
Tear Film Evaluation: Tear film evaluation assesses the quantity and quality of tears to identify underlying dry eye syndrome, a common contributor to digital eye strain. Tear film abnormalities can lead to ocular surface irritation, redness, and discomfort during prolonged screen use.
Strategies for Addressing Digital Eye Strain
Effective management of digital eye strain involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, ergonomic adjustments, and technological interventions tailored to individual needs. Here are some strategies for addressing digital eye strain:
Follow the 20-20-20 Rule: To reduce eye fatigue and strain, take regular breaks from screen time by following the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look away from the screen, and focus on an object at least 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
Adjust Screen Settings: Optimize screen brightness, contrast, and font size to enhance visual comfort and reduce glare. Use dark mode or night mode settings on digital devices to minimize blue light exposure, especially during evening hours.
Maintain Proper Posture: Ensure ergonomic workstation setup with the screen positioned at eye level and arm’s length away, and use an adjustable chair with adequate lumbar support to maintain a comfortable seated posture.
Blink Regularly: Blink frequently while using digital devices to lubricate the eyes and prevent dryness. Consider using lubricating eye drops or artificial tears to relieve dry eye symptoms and maintain ocular surface health.
Practice Good Lighting: Position digital screens away from direct sunlight and minimize glare from overhead lighting or reflective surfaces. Use task lighting to illuminate work areas evenly and reduce eye strain.
Consider Blue Light Filters: Invest in blue light-filtering glasses or screen filters to reduce exposure to harmful blue light emitted by digital screens. These filters can help alleviate digital eye strain and promote better sleep quality.
Schedule Regular Eye Examinations: Visit an eye care professional for routine eye examinations to monitor vision changes, screen for underlying eye conditions, and receive personalized recommendations for managing digital eye strain.
Implement Digital Detoxes: Take periodic breaks from digital devices and engage in screen-free activities such as outdoor exercise, reading physical books, or practicing mindfulness meditation to reduce reliance on screens and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
Digital eye strain is a prevalent condition affecting individuals who spend extended periods in front of digital screens. By understanding the causes, symptoms, assessment methods, and management strategies for digital eye strain, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce visual discomfort, optimize screen use, and promote long-term eye health and wellness in the digital age. Prioritizing regular eye examinations, adopting ergonomic practices, and implementing lifestyle modifications can help mitigate the impact of digital eye strain and enhance overall quality of life.